Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI and sometimes known as Brittle Bone Disease) is a genetic bone disorder. People with OI are born without the proper protein (collagen), or the ability to make it. People with OI either have less collagen than normal or the quality is poorer than normal. As collagen is an important protein in bone structure, this impairment causes those with the condition to have weak or fragile bones.
In OI either the collagen is of normal quality but is produced in insufficient quantities or the collagen is abnormal in structure. This leads to
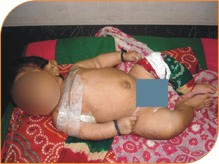
- Bones fracture easily and may heal in deformed position
- Children may develop abnormal spinal curvature
- They have loose joints and poor muscle tone
- A few patients have light blue colour of eyes
- They may develop early loss of hearing in some cases.
- A few cases are associated with abnormal teeth a condition called Dentogenesis imperfecta
Treatment
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy used to strengthen muscles and improve motility in a gentle manner, while minimizing the risk of fracture. This often involves hydrotherapy and the use of support cushions to improve posture.
Children often develop a fear of trying new ways of moving due to movement being associated with pain. This can make physiotherapy difficult to administer to young children. The physiotherapist will teach parents how to handle very small babies without causing pain to them.
Bisphosphonates
A group of medicine called Bisphosphonates (BPs), particularly those containing nitrogen, are being increasingly used in patients with IO to increase bone mass and reduce the incidence of fracture. BPs can be dosed orally (e.g. alendronate) or by intravenous injection/infusion (e.g. pamidronate).
BP therapy is being used increasingly for the treatment of OI. It has proven efficiency in reducing fracture rates in children,
While decreasing fracture rates, there is some concern that prolonged BP treatment may delay the healing of OI fractures, although this has not been conclusively demonstrated.
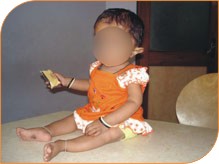
Same child after Pamidronate therapy has considerable reduction in fracture rate.
Pamidronate is usually administered as an intravenous infusion, lasting about three hours. The therapy is repeated every three to six months, and lasts for the life of the patient. Common side effects include bone pain, low calcium levels, nausea, and dizziness.
Surgery
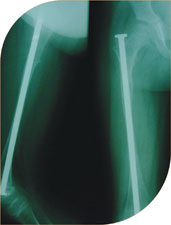
Roding of bones of the bones is one of the most common surgeries performed in OT. Rods put in the canal of the bone can give them additional strength and prevent frequent fractures.
Special types of rods called Telescoping rods are the latest addition for the treatment of OI. This is a special rod which self elongates with growth of the child and increase in height. This prevents repeated surgeries to change fix rods which become short after height is gained by the child.
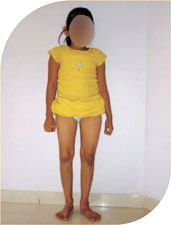
Four year old girl with OI came with repeated fractures in both femora. One side she had surgery which failed and she developed bowing of her right thgh. The nail put in her right femur had come out deforming her right thigh.
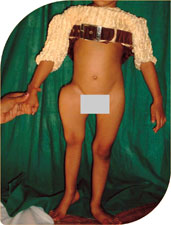 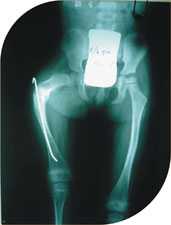
She was treated with telescoping nails and she has complete correction of deformity and is fracture free for last four years. She is on oral bisphosphonates.
|

